About the application of Dot Code two-dimensional code
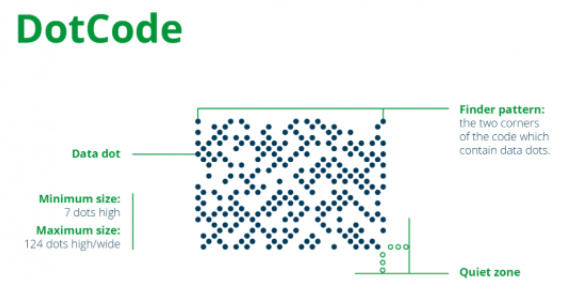
Dot Code is a matrix two-dimensional code, a variant of DPM two-dimensional code. It is a two-dimensional code issued by the International Article Coding Association (GS1) for identifying small and difficult-to-mark items. It can be prepared up to 150 binary bytes, and other compression coding methods can also be used to represent more text data or digital information. Compared with bar Code, Dot Code two-dimensional code can carry more information, which is more suitable for the occasion of different printing area requirements and the occasion of needing more items properties, especially high-speed inkjet printers and laser printers or laser engraving machines.
DotCode uses matrix Dot as the carrier of additional information. The two-dimensional code has variable size, diverse module shapes, strong error correction ability, and can be quickly identified. DotCode can encode other attributes (such as serial number, production date, expiration date, etc.) of an item associated with the Global Trade Goods Code (GTIN) into a QR code. It will enable products that are difficult to label, such as fresh food and produce (meat, cooked food, produce), to have unique identification and identification. Dot Code can also carry all other GS1 application identifiers in addition to (GTIN), such as batch numbers and expiration dates, production dates, etc., to support product certification and tracking.
Main features of DotCode
1. Matrix two-dimensional code with variable ranks
2. Row number: 5-200, column number: 5-200
3. Can be used alone or in combination with GS1 DataBar
4. There are three data compression modes: text, binary, and digital
5. Maximum data capacity 450 (letters), 900 (pure numbers)
DotCode The two-dimensional code is widely used in various fields. These include logistics, warehousing, libraries, banking, POS cashier systems, health care, retail goods, clothing, food services and high-tech electronics, and are now being used on a daily basis in a number of new projects.