DotCode two-dimensional code
DotCode is a two-dimensional barcode that encodes data as points in a rectangular array.
In high-speed manufacturing industries, DotCode can be used as an alternative to other QR codes to facilitate item serialization, allowing products to be tracked through the global supply chain.
DotCode was developed by Dr. Andrew Longacre and published as an official specification by the global industry standards body AIM in 2009.
Dotcodes are public domain codes, which means they are copyright-free and have no royalties, so organizations of all kinds do not need authorization to print or use them.
Like other QR codes, DotCode has error correction capabilities using the Reed-Solomon correction algorithm, which can be used to detect and recover missing data in QR codes. This means that if part of the code is lost or corrupted, DotCode can still be read.
What does DotCode look like?
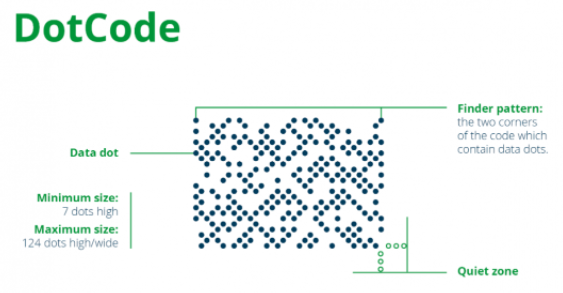
Unlike many other QR codes, DotCode is usually rectangular in shape. The data in DotCode is encoded as "data points". The data points can be square or round and lie on the diagonals of the rectangular grid.
The size and direction of DotCode is flexible, but the code must have an odd number of points for height and width.
DotCode can print in a dark color on a light background or in a light color on a dark background, as long as there is enough contrast to ensure readability.
The minimum size of DotCode is 7 points high, and theoretically there is no maximum size, but the practical limit that most printing techniques can achieve is 124 points in any direction.
Like other QR codes, DotCode has an "image finder graph" that can be seen at two corners of the code containing data points -- points that are positioned so that a data reader or scanner knows where to start reading data.
When DotCode is printed, it must be surrounded by a "static area" that is three dots wide. This blank space ensures that the scanner can efficiently scan and read the code without recognizing any additional printed content.